Gout is a painful condition that results from crystals of uric acid depositing in tissues of the body. Gout is characterized by an overload of uric acid in the body and recurring attacks of joint inflammation (arthritis). Chronic gout can lead to deposits of hard lumps of uric
acid in and around the joints, decreased kidney function, and kidney stones.
acid in and around the joints, decreased kidney function, and kidney stones.
Uric acid is a substance that normally forms when the body breaks down waste products (called purines). Uric acid is usually dissolved in the blood and passes through the kidneys into the urine. For people with gout, the uric acid level in the blood is so high that uric acid crystals form
and deposit in joints and other tissues. This causes the joint lining to become inflamed, resulting in sudden and severe attacks of pain, tenderness, redness and warmth. After several years, the crystals can build up in the joints and surrounding tissues, forming large deposits, called tophi. Tophi look like lumps under the skin and are often found in or near severely affected joints, on or near the elbow, over the fingers and toes, and in the outer edge of the ear.
Gout has the unique distinction of being one of the most frequently recorded medical illnesses throughout history. It is often related to an inherited abnormality in the body's ability to process uric acid. Uric acid is a product of broken-down purines, which are part of many foods we eat. An abnormality in the body's handling of uric acid can cause attacks of painful arthritis (gout attack), kidney stones, and blockage of the kidney filtering tubules with uric acid crystals, leading to kidney failure. On the other hand, some patients may only develop elevated blood uric
acid levels (hyperuricemia) without having arthritis or kidney problems. The term "gout" is commonly used to refer to painful arthritis attacks, which are usually extremely
painful attacks with a rapid onset of joint inflammation. The joint inflammation is precipitated by deposits of uric acid crystals in the joint fluid (synovial fluid) and joint lining (sy! novial lining). Intense joint inflammation occurs as white blood cells engulf the uric acid crystals and
release inflammatory chemicals, causing pain, heat, and redness of the joint tissues.
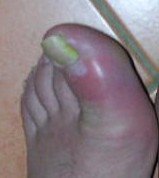
Gout usually affects only one or two joints at a time - most often the feet and ankles. The ball of the big toe is the most common site. Without treatment the attack subsides in a week or so, and when patients first develop gout, there may be intervals of many months or even years between
attacks. As time goes by, these tend to become more frequent and more severe and eventually many joints may be involved, sometimes all at the same time. With progressive joint damage, a state of chronic or continuous joint disease (chronic gout) may develop, causing disability and crippling. Gout affects mostly men and is very rare in women until after menopause when it is seen quite often. Some surveys have shown it to be present in up to 10% of adult males.
J M Nor
http://www.Nor-OnlineBiz.com